ITS VERY IMPORTANT TO US @ THATPLUM TO GIVE OUR FOLLOWERS INFORMATION ON HOW TO HAVE A DAILY HEALTHY LIFESTYLE.
FIBROIDS/UTERINE
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous (benign) tumors that develop in the womb (uterus), a female reproductive organ.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
Uterine fibroids are common. As many as 1 in 5 women may have fibroids during their childbearing years (the time after starting menstruation for the first time and before menopause). Most woman who have fibroids tumors never even know it,
unless they are discovered during the course of a routine examination. Half of women have fibroids by age 50.
Fibroids are rare in women under age 20. They are more common in African Americans than Caucasians.
The cause of uterine fibroids is unknown. However, their growth has been linked to the hormone estrogen. As long as a woman with fibroids is menstruating, a fibroid will probably continue to grow, usually slowly.
Fibroids can be so tiny that you need a microscope to see them. However, they can grow very large. They may fill the entire uterus, and may weigh several pounds. Although it is possible for just one fibroid to develop, usually there are more than one.
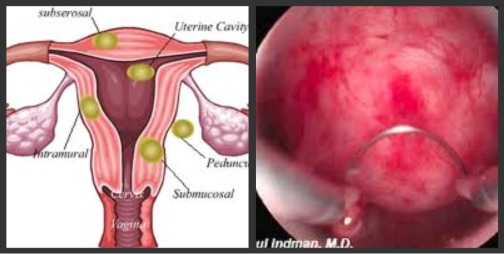
Fibroids are often described by their location in the uterus:
- Myometrial — in the muscle wall of the uterus
- Submucosal — just under the surface of the uterine lining
- Subserosal — just under the outside covering of the uterus
- Pendunculated — occurring on a long stalk on the outside of the uterus or inside the cavity of the uterus
Symptoms
More common symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
- Bleeding between periods
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia), sometimes with the passage of blood clots
- Menstrual periods that may last longer than normal
- Need to urinate more often
- Pelvic cramping or pain with periods
- Sensation of fullness or pressure in lower abdomen
- Pain during intercourse
Complications
Complications of fibroids include:
Severe pain or excessively heavy bleeding that may require emergency surgery
Twisting of the fibroid, which causes a blockage in nearby blood vessels feeding the tumor (surgery may be needed)
Anemia (low red blood cell count) if the bleeding is very heavy
Urinary tract infections, if pressure from the fibroid prevents the bladder from fully emptying
Cancerous changes called leiomyosarcoma (rare)
In rare cases, fibroids may cause infertility. Fibroids may also cause complications if you become pregnant, although the risk is thought to be small:
Some pregnant women with fibroids may deliever a premature baby because there is not enough room in the womb.
A c-section may be needed if the fibroid blocks the birth canal or causes the baby to be in a dangerous position.
Some pregnant women with fibroids have heavy bleeding immediately after giving birth.
- I’m not a medical doctor so any sharing of health educational information in this website should be taken as just that — the sharing of educational information. Please see the disclaimer link.